Meaning
Mental status examination is a snap shot
of a person’s psychological status combined with the observations and
interpretations of Nurse at that point of time.
Uses
ü Helps
in identifying the psychological status of a person
ü Act
as a basis for initiating and maintaining therapeutic assistance
ü Serves
as a record for evaluating the change in psychological status comparing to a
previous state.
ü Helps
in assessing the effectiveness of health care rendered
Guidelines
·
Data collected through the Mental Status
Examination represents the psychological status of only a shorter period.
·
Both subjective and objective should be
given due consideration.
·
While doing mental status examination
person’s educational and cultural background should be kept in mind for
accurate interpretation.
·
After each component Inference should be
noted.
Components
I. Identification data
Name
Age:
Sex:
Hospital
number:
Diagnosis:
Date
of admission:
Date & Time:
Venue:
Language of interview:
Time taken for interview:
II.
General
appearance
a) Posture
& Facial expression: stooped posture/erect posture; facial expression-
sad/pleasant/blank
b) Grooming:
well groomed/ not groomed well
c) Clothing:
appropriate to gender/ inappropriate to gender
d) Body
build: moderately built.
e) Eye
to eye contact: maintained/ not maintained
f) Attitude
towards the examiner: co operative/ not co operative
g) Handedness:
Right/Left handed
h) Manner
of relating: co operative and good.
i) Rapport:
able to establish & maintained/ unable to establish
j) Motor
behaviour:
Echopraxia: Repetition of movements of one
individual by another individual which are associated with mental illness. eg:
hopping, tapping, touching when patient sees someone is doing that. Most
commonly seen in catatonic schizophrenia and Tourette syndrome.
Catatonic features:
Waxy flexibility (Cerea flexibilitas): A
condition in which a person can be positioned in any particular way while
examination and it is maintained. Person’s body will be felt like wax which can
be moulded in desirable way.
Negativism: Resistance to all instructions
without any intention. Eg: When a person is asked to give his hands taking it
backward.
Stereotypy: Pattern of
speech or action which is repeated. Eg: Flapping hands, marching in one place.
It differ from tics as tics will be there for short periods but stereotypy may
last for years.
Dystonia: Continuous, slow contractions of
chest, abdomen & limbs which is caused by some medications.
Chorea: Random and involuntary quick,
jerky, purposeless movements.
Hyperactivity: Restless, aggressive,
destructive activity.
II.
Mood
& Affect
Qn: How do you feel nowadays?
a) Mood-
“A pervasive and sustained emotion subjectively experienced and reported by a
patient and observed by others.”
depressed, irritable, anxious, angry,
expansive, euphoric, guilty, perplexed, labile
In mania patients it may be elevated,
expansive or irritable. Elevated mood is characterized by excited, euphoric,
happy and high feeling of good. Expansiveness is indicated when the client
shows high interest in social and interpersonal interactions.
b) Affect-
It is the expression of emotion which was observed by the examiner. In certain
cases it will not be correlated with the mood. Blunted affect is commonly seen
in Schizophrenia.
(range, intensity, stability,
appropriateness)
III. Speech
Eg: How do you celebrate (mention any
festival) at home?
(Quantity, talkative, voluble,
spontaneous, rapid or slow, pressured, Poverty of speech, stuttering,
disprosody, Echolalia)
Stuttering- Repetition of syllables, words
or pronouncing elongation.
Disprosody-Is an neurological disorder in
which there will be variation in speech tone, stop and pronunciation
Echolalia- Repetition of one person’s
speech by another person is called as echolalia. Eg: If we ask the patient “Had
your food?” His reply will be “Had your food?”
IV.
Perception
Hallucination:
Wrong sensory perception without an external stimulus; which may be associated
with delusional interpretation of hallucinatory ideas.
a) Auditory
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception of voices, music and noise without an
external stimulus. Eg: Hearing people talking, birds chirping when it is not
there.
b) Visual
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception of clear and vague images without an
external stimulus. Eg: Seeing shapes, light or people when it is not there in
real.
c) Olfactory
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception of smell without an external stimulus.
Eg: Smelling poisonous gas in room which is not real.
d) Gustatory
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception of taste without an external stimulus.
Eg: Taste of poison in food which is not real.
e) Tactile
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception of touch/ crawling over the body without
an external stimulus. Eg: feeling like bugs are crawling over the body.
Commonly associated with drug abuse.
a) Hypnagogic
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception which arises when the patient is about
to sleep.
b) Hypnapompic
hallucination- Wrong sensory perception which arises when the patient is about
to come out from sleep.
Qn:
Do you hear some voices when you are sitting alone?
Do
you see some images/ pictures when you are alone?
Do
you smell something abnormal in your surroundings?
Do
you find any change in taste in your food?
Do
you find something is crawling over your body?
If
answer to any of the above the question is “yes” elicit further on it.
In case of
auditory hallucination ask for the type of voice, is it a noise or sound.
If it is a person talking ask
· How
many members are talking
· Are
they talking to the patient (second person auditory hallucinations)or talking
among themselves( third person auditory hallucinations)
· Is
it a male or female voice?
· Whether
patient knows the person?
· Content
of voice?
· What
time it is being heard?
Illusion:
Misinterpretation of an external stimulus is called as illusion
Eg: Verbalizing IV tubing as snake.
It is being observed or the patient reports
without asking. Commonly seen in patient who are delirious.
V. Thought
a)
Form
· Circumstantiality-
It is a pattern of thought in which the person delays to come to the point of
talk, often talk irrelevant topics before coming to the point of talk. Eg: When
we ask about where is his wife patient talks about his place, his home and at
last telling about his wife.
· Flight
of ideas- This is rapid pattern of thought in which the person shifts from one
topic to another topic which are connected to each other. It is often seen in
mania and ADHD.
· Loosening
of associations- It is a type of thought disturbance in which flow of thought
shift from one topic to another which are not related to each other.
· Irrelevance-
Giving answers which are not related to the question. Sometimes the person may
not attend to the question.
· Neologism-
It is coining of new words by the patient which doesn’t have a meaning.
Eg:Staycation
· Perseveration-It
is repetition of same response of a previous stimulus even when a new stimulus
is introduced. Eg: When we ask” What you had in the morning?” Patient replies
“Idli” for next question “Who is with you?” Patient again responds “Idli”
· Thought
block- It is sudden stoppage on flow of thought before one thought is complete.
· Tangentiality-
In this pattern of thought disturbance person will not come to the point of
thought about which he is supposed to think.
· Thought
insertion- This is subjective feeling that someone is inserting thoughts into
his mind.
· Thought
withdrawal- It is a subjective feeling that someone is removing his/her
thoughts.
· Thought
alienation- The patient has the experience that his thoughts are being
controlled by an external agency.
b)
Content
· Ideas
of reference- It is incorrect thinking that unrelated incidents have a personal
reference. Person who sees two people are talking will think that they are
talking about him.
· Delusion-These
are false unshakeable beliefs which are not amenable to reasoning and not
consistent with the person’s intelligence, social and cultural context.
· Delusion
of persecution- False unshakeable belief that he/she is being spied up on, cheated
or persecuted by others which is not amenable to reasoning and not consistent
with the person’s intelligence, social and cultural context. Eg: Person
believes that his relatives or others are trying to kill him or cheat him”
· Delusion
grandiosity- False unshakeable beliefs about his importance, power or identity
which are not amenable to reasoning and not consistent with the person’s
intelligence, social and cultural context. Eg: Person strongly believes that he
has some special power to control the world or he is god.
· Hypochondriasis-
A subjective thought that he is ill without any organic pathology. These
patients will go for consulting so many doctors as they will not be accepting
that they are not ill.
· Worthlessness-
A subjective thinking he/she is not worthy in anything.
· Hopelessness-
Thinking that there is no hope about future life.
· Delusion
of guilt- False unshakeable belief that he had done some mistake which is not
amenable to reasoning and not consistent with the person’s intelligence, social
and cultural context.
· Delusion
sin- False unshakeable belief that he is a sinner which is not amenable to
reasoning and not consistent with the person’s intelligence, social and
cultural context.
· Delusion
of love (Erotomania)- False unshakeable belief that someone is deeply in love
with her which is not amenable to reasoning and not in accordance with the
person’s intelligence, social and cultural context.
· Delusion
of control- False unshakeable belief that some external agency is controlling
his thoughts or feelings and is not amenable to reasoning which is not in
accordance with the person’s intelligence, social and cultural context.
· Delusion
of infidelity- False unshakeable belief of person that his partner is not
faithful which is not amenable to reasoning and not in accordance with the
person’s intelligence, social and cultural context.
· Phobia-
These are persistent, pathological and irrational fear of a specific stimulus
and which will lead to the avoidance of the stimulus.
Eg: Fear of closed spaces- Claustrophobia.
· Somatisation
delusions- False unshakeable belief that involves the functioning of the body
which is not amenable to reasoning and not in accordance with the person’s
intelligence, social and cultural context.
· Suicidal
ideas, homicidal ideas
· Pre occupations-Centring of thought around a
particular idea.
· Obsessions-
These are the repetitive thoughts which are irresistible by the person and
produces anxiety.
VI. Sensorium & Cognition
a)
Alertness& Consciousness
· Clouding
of consciousness- Alteration in perception and attitudes with partially clear
mind.
· Stupor-
It is unresponsiveness to an external stimulus.
· Coma-
Profound degree of unconsciousness.
· Lethargy
· Alertness- Attentiveness to external cues.
· Fugue-Wandering
state with loss of memory
b)
Orientation
Time,
date, day, month, year, place, person
Qn: What may be the approximate time now?
( Without looking at the clock?)
Qn: What is today’s date?
Qn: Which day is today?
Qn: Which is this month?
Qn: Which is this year?
Qn: Where are you now?
Qn:Who am I/ Who is sitting next to you?
c)
Attention& Concentration
· Concentration-
100-7, 40-3, 20-1: 5 steps. Ask the patient to subtract 7 from 100 5 steps, if
he is not able to do it go for 40-3 or 20-1, Month backwards, days of week
backwards,
· Attention-
digit forward & backwards. Give a 5 digit number and ask him repeat it
backward Eg: 72918, 81927.
d)
Memory
· Immediate
( within 5 minutes)
o
Show five unrelated objects ask the
patient to name them. After naming hide it from patient’s vision. Ask
afterwards to remember and tell those names.
o
Give a five digit number which is not in
sequence eg: 72918
· Recent(
within past few days)
o
What you had for last night dinner?
o
Who visited you yesterday?
· Recent
past (Within 6 months)
o
Which festival you celebrated last month?
o
When did you go to temple last?
o
Which friend you visited last month?
· Remote
( more than 6 months)
o
Which year you passed SSLC?
o
Which year you started working?
o
What was your primary school teacher’s
name?
e)
Abstractability
· Similarities
Eg: What are the similarities between pen &
pencil/ table & chair?
· Dissimilarities
Eg: What are the dissimilarities between pen&
pencil?
Two pictures can be given and can be asked to mark the
similarities and dissimilarities.
· Proverbs
Ask the patient to tell a proverb and explain its
meaning.
f)
General information
· It
should be asked based on the educational and occupational background of the
person.
Eg: For a housewife “How much 1kg Rice cost?”
g)
Calculation
Verbal & written
For people who
are not educated simple calculation can be given. Eg: You went to a shop and
bought 10Rs. soap and you gave 20 Rs. How much balance you should get?
h)
Intelligence
Based on comprehension, abstraction, general
information and calculation
VII. Impulse control
It
observed during the interview and from history whether he is able to control
his impulses. Common impulses are Anger, anxiety, sexual impulses and fear.
VIII. Judgement
· Test
o
It is assessed by giving a situation to
the patient and asking him how he will respond to it.
Eg: If you see a house getting fire what you will do?
· Personal
o
Qn: What you will do after discharge?
· Social
o
How the person interacts with others in
the ward is observed & based on history.
IX. Insight
Present
Absent
Partially
present
Grading
1.
Denies the illness completely.
2.
Patient has slight awareness that he is sick and
requires help, but he denies it at the same time
3.
Aware that he is sick but attributes it on other people,
on factors which are external, or on biological factors
4.
Aware about illness that it is because of something
which is unknown within him.
5.
Intellectual insight: Patient accepts that he is
ill and that symptoms or inability in adjusting with society are the result of
his own particular irrational feelings or disturbances. But will not apply this
knowledge in his future experiences.
6.
True emotional insight: Patient is emotionally
aware about his intention and feelings within him and about persons who are
important in his or her life. This will lead to basic changes in his behaviour.
X.
Conclusion:
It includes summary of
all inferences.
References
1.
Ahuja .N.A short text book of psychiatry.5th
ed. New delhi: Jaypee publishers;2006.
2.
Stuart GW. Principles & Practice of Psychiatric Nursing.
9th ed. USA: Mosby publication; 2009.
3.
Keltner NL,Schwecke L H,Psychiatric
nursing.1st ed.mosby;mosby:2003.
4.
Kaplan. Synopsis of psychiatry.9th
ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 2009.
Examples-
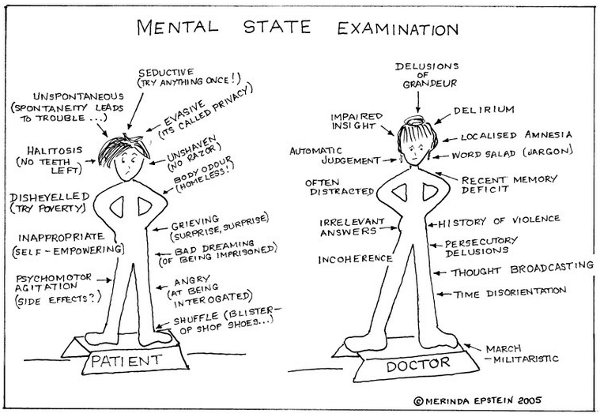
 |
| MSE in Mania |
 |
| MSE in Depression |
These above two pictures taken from - This source.
Mnemonic:
Mental State Examination
ASEPTIC
· Appearance / Behaviour
· Speech
· Emotion (mood and affect)
· Perception (hallucinations, illusions)
· Though (content, form)
· Insight
· Cognition (AMT, MMSE)














COMMENTS